- Overview
- Types of Chronic Pain
- Causes of Chronic Pain
- Chronic Pain Symptoms
- Chronic Pain Diagnosed
- Treatment For Chronic Pain
- Chronic Pain Home Remedies
- Chronic Pain – Conclusion
Pain is a common reason many people seek health care, and it is a leading cause of disability in the world. It can take a toll on the mental and physical health of a person. Some pain persists for longer than 3 months; such pain is termed chronic pain.
In this context, we have discussed about chronic pain in detail.
Chronic Pain – An Overview
Chronic pain is a type of pain that lasts for a long period, usually for more than three months. It doesn’t have a permanent cure and can last for even years.
Chronic Pain Facts:
- More than men, women are likely to suffer from chronic pain.
- 8 in 10 patients with chronic pain are impacted by symptoms of depression
- Among American adults, arthritis is the most commonly reported cause of chronic pain.
- Every year, chronic pain costs upto an amount of $635 billion.
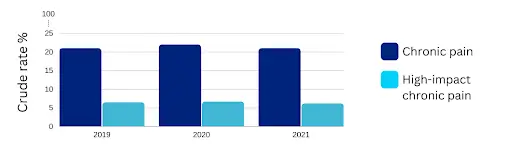
Between 2019 and 2021, the prevalence of chronic pain in the United States ranged from 20.5% to 21.8% (among adults), and the high-intensity chronic pain (pain that is persistent with substantial restriction of life activities) prevalence was 6.9% to 7.8%, as graphically represented below.
Types of Chronic Pain
Chronic pain can be divided into:
- Neuropathic pain
- Nociceptive pain.
Neuropathic Pain:
Neuropathic pain is a type of chronic pain that is caused by nerve damage or tissue injury. Neuropathy is caused by damage to the nerves themselves instead of a physical injury. One of the main causes of this type of pain is diabetes.
Sources of Neuropathic Pain:
Nine sources of neuropathic pain are:
- Diseases,
- Infections,
- Accidents,
- Surgery,
- Arthritis,
- Parkinson’s disease,
- Facial Nerve Problems,
- Complex Regional Pain Syndrome,
- Carpal tunnel syndrome.
Nociceptive Pain
Nociceptive is a chronic body pain that detects noxious stimuli by nociceptors, which are carried through the CNS, or central nervous system, for the body to protect itself from any kind of harm.
Nociceptors are receptors that are present in various parts of the body, such as somatic and visceral tissues.
Nociceptive pain can be classified into:
- Visceral pain.
- Somatic pain.
Visceral Pain:
Visceral pain results from internal organs, in the chest cavity or the abdomen specifically. It can come from referred pain (it can be felt in a part of the body rather than its original source). For example:
- Migraines
- Badder pain
- Endometriosis.
Somantic Pain:
Somatic pain turns out from injuries in the outer body, like muscles, tendons, joints, bones, or skin.
Examples of somatic pain include joint injuries or arthritis [2] [3].
Causes of Chronic Pain
Chronic pain has several root causes. Some of the common origins of chronic pain include:
- Endometriosis:
It is a painful condition that causes tissue comparable to the uterine lining to grow outside the uterus.
- Back pain:
One of the main causes of chronic pain is back pain. Back pain is defined as the physical discomfort in the spine or back of the body.
- Cancer
Chronic pain can be associated with cancer as a side effect of its treatment or the disease itself.
Cancer is a disease that causes the uncontrollable growth of cells in the body.
- Interstitial cystitis
Interstitial cystitis, or bladder pain syndrome, is a condition characterized by burning, pain, and pressure in the urinary bladder, along with urgency and frequency. [4].
Chronic pain symptoms
Chronic pain can feature psychological and physical symptoms, such as the ones as follows:
Physical Symptoms of Chronic Pain
Six physical symptoms of chronic pain are:
- Aching, burning, shooting, or electrical shock-like pain.
- Discomfort in the muscles or joints.
- Loss of energy
- Difficulty sleeping due to pain.
- Decreased mobility.
- Pain that may be widespread or local to one area, such as a single joint or many.
Psychological Symptoms Of Chronic Pain
Seven psychological symptoms of chronic pain are listed below:
- Anxiety or depression.
- Tension and stress.
- Reduced interest in participating in social activities.
- A feeling of isolation because of the pain.
- Fear of pain not going away or worry about pain becoming worse.
- Worry over job loss due to a chronic pain condition.
- Difficulty concentrating and remembering things [4].
How Is Chronic Pain Diagnosed?
During the diagnosis process, your doctor will check your health history and do a physical test, but before that, you’ll be asked a few questions about your pain. For example:
- In which location is your pain?
- Since how long you’re suffering from chronic pain?
- Have you ever experienced chronic pain before?
Based on the answers to the questions above and the results of various physical tests, your healthcare provider will recommend you to have diagnostic tests (one or more).
These include:
- Blood tests:
Blood tests are helpful in providing ideas about what is the cause of pain in the body. They show if there is any sign of inflammation, infection, or abnormalities in an organ.
- X-rays:
X-rays are radiations known as electromagnetic waves that create pictures of the inside of your body. It helps to show bone problems such as fractures or arthritis.
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging:
This test is helpful in showing compressed nerves, organs, or soft tissues and is helpful in providing about the main cause of certain types of pain.
- CT scan:
Computed tomography, also known as a CT scan, is a test that shows internal organs and soft tissues and is helpful in detecting various types of cancer.
- Nerve conduction tests:
These tests help doctors identify abnormalities in both muscles and nerves. This procedure is carried out by giving an electrical shock (small) to a nerve, and the electrical signal traveling down the nerve is measured.
How To Deal With Chronic Pain – Treatment For Chronic Pain
There are various things that you can do to manage chronic pain. Some of the ways are laid down below:
Medication for Chronic Pain:
Some common medicines prescribed for chronic pain are:
- Antidepressants
- Pain relievers
- Anticonvulsants.
Some other medical treatments to manage chronic pain include:
Nerve blocks:
In this treatment, a doctor injects an anesthetic near the region of your pain to reduce feeling in that area. Nerve blocks can sometimes locate the source of your pain and can provide diagnostic information.
Epidural steroid injections:
This injection comprises an anti-inflammatory medicine – a corticosteroid or steroid- that is injected into the space around your spinal nerves, known as the epidural space, to treat chronic pain caused by inflammation or irritation of spinal nerve roots.
Therapies for Chronic Pain
There are various therapies that one can use to relieve chronic pain, two of them are mentioned below:
CBT or Cognitive-behavioral therapy:
This method teaches you ways to cope with pain and helps you think differently about pain.
Occupational therapy:
This therapy teaches you how to do tasks differently every day to avoid injury and lessen pain.
Alternative Treatments For Chronic Pain
Alternative treatments to manage chronic pain are –
Acupuncture:
Acupuncture is effective in treating chronic pain such as musculoskeletal, headache, and osteoarthritis pain, according to a review by Andrew J. Vickers et al. published in 2018 [6].
Aromatherapy
Aromatherapy is a therapy that makes use of essential aromatic oils by inhaling or through the skin [7] [8].
According to research, aromatherapy can cause an instant decrease in chronic pain.
Chronic Pain Home Remedies

Home remedies for chronic pain are:
Exercise
While doing physical activities, the body produces hormones that decrease the perception of pain, known as endorphins, which are crucial for managing chronic pain.
Fish Oil
Fish oil is a supplement that is rich in omega-3 fatty acids. Omega-3 fatty acids are important because they help to build brain cells, and also perform other essential body functions.
Fish oil is found to be an effective option for managing chronic pain because it has anti-inflammatory properties as well.
In one study, which was published in 2006, many people were asked to take 1200 mg of fish oil with eicosapentaenoic and docosahexaenoic acids if they were suffering from back and neck pain. After 75 days, 125 people reported back and informed they had stopped taking pain reliever medicines [9].
Turmeric
Turmeric consists of curcumin, which has anti-inflammatory properties and helps in reducing chronic pain.
Heat and Ice
Applying heat and ice directly to the sites of pain has been an effective way of reducing pain. Applying ice to reduce inflammation and swelling shortly after you experience a strained tendon, ligament, or muscle may bring relief.
Interestingly, once the inflammation has reduced, heat can help decrease the stiffness that comes with strain and sprain [10].
Chronic Pain – Conclusion
Life with chronic pain is not easy, and there is no permanent cure for this type of pain, but by working with your doctor, finding the right treatment, and making smart and healthy choices, you can make improvements significantly.
FAQs
Give an example of chronic pain?
Is chronic pain caused by trauma?
Which age group is most prone to chronic pain the most?
What is Chronic pain syndrome?
Can chronic pain be managed?
References
-
29 Chronic Pain Statistics: US & Global Prevalence, thegoodbody
-
Different Types of Chronic Pain, southernpainclinic
-
Types and Causes of Chronic Pain, shepherd
-
What Is Chronic Pain? Causes, Symptoms And Treatment, forbes
-
A chronic pain syndrome is the combination of chronic pain and the secondary complications that are making the original pain worse.
-
Acupuncture for Chronic Pain: Update of an Individual Patient Data Meta-Analysis, NCBI
-
Chronic Pain, clevelandclinic
-
Benefits of Using Aromatherapy to Help Reduce Chronic Pain Symptoms, southernpainclinic
-
Omega-3 fatty acids (fish oil) as an anti-inflammatory: an alternative to nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs for discogenic pain, PubMed
-
6 Cheap, Natural, and Quick Chronic Pain Remedies, everyday health

